Inner Workings of ChatGPT-4 AI Attention Blocks, Feedforward Networks, and More
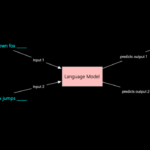
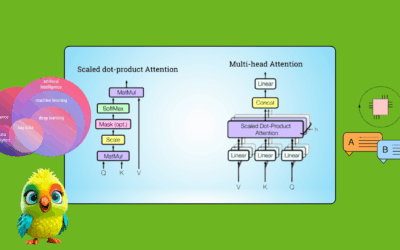
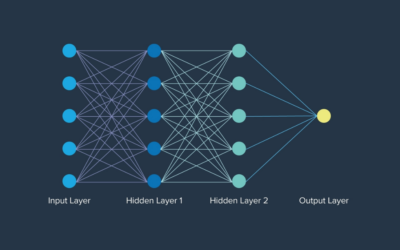
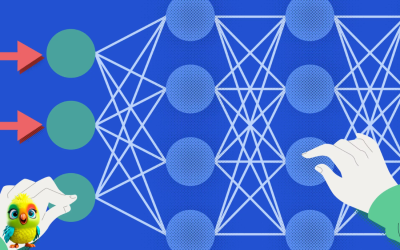
At its core, ChatGPT-4 is built on the Transformer architecture, which revolutionized AI with its self-attention mechanism. Below, we break down the key components and their roles in generating human-like text. 1. Transformer Architecture Overview The Transformer consists of encoder and decoder stacks, but GPT-4 is decoder-only (it generates text autoregressively). Key Layers in Each Block:…