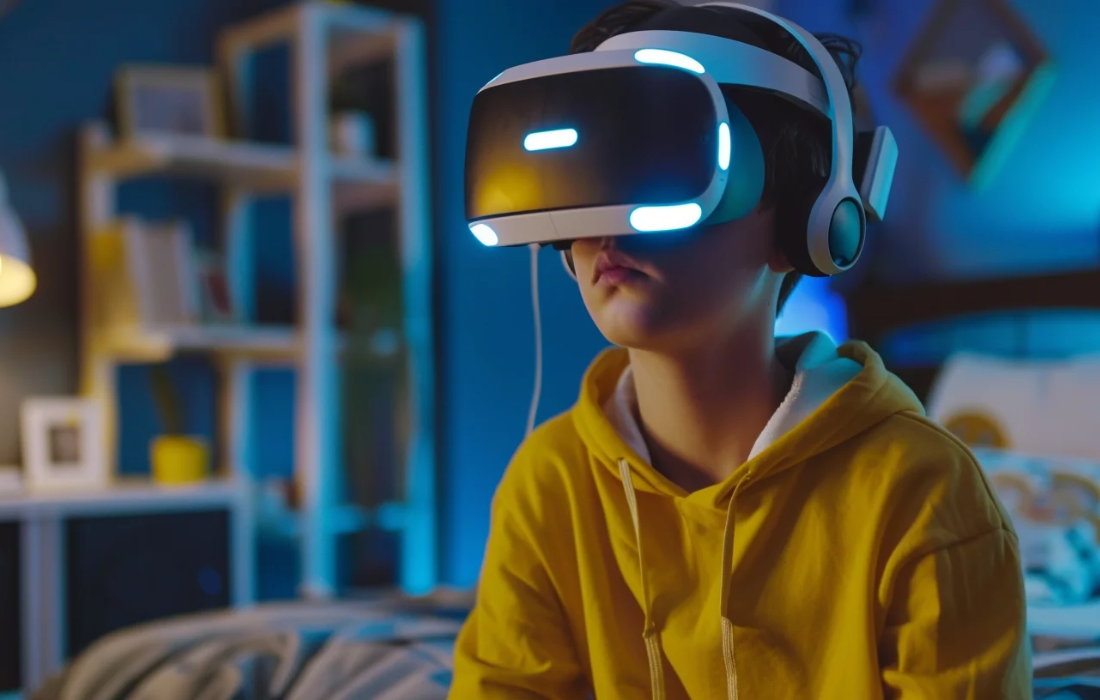
Virtual reality (VR) has evolved from an experimental concept to a mainstream technology, offering innovative ways to engage users across different industries. It creates simulated environments that users can interact with in a manner that mimics the real world, providing an immersive experience that stimulates multiple senses, including sight, sound, and touch. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the basics of virtual reality, its main types, features, applications, and future trends.
What is Virtual Reality?
At its core, virtual reality is a computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional environment that users can explore and interact with in a way that approximates real life. Unlike traditional interfaces where users are passive recipients of information, VR places the user inside a fully immersive, interactive experience. The more immersed users are in this environment, the more they can suspend disbelief and accept it as real, even if the scenario is fantastical. VR technology typically requires specialized equipment such as headsets, motion controllers, and gloves, but advances are making VR more accessible with mobile devices and affordable VR headsets.
The Different Types of Virtual Reality
VR systems can vary significantly depending on the technology used and the intended use case. While the technology is still evolving, virtual reality can generally be classified into six categories:
- Non-Immersive VR: This type of VR is typically accessed through a computer screen, where users can interact with a 3D environment using a keyboard or mouse. Non-immersive VR offers limited interaction, and the user is not fully immersed in the virtual world. An example would be a video game or a website that allows users to design their living space.
- Semi-Immersive VR: Semi-immersive VR offers a partial immersion experience, where the user is more engaged visually, often through a headset or specialized glasses. This type does not fully engage the user in a physical sense, but it provides a 3D environment that responds to the user’s input. Flight simulators, used by military or airlines for pilot training, are a prime example.
- Fully Immersive VR: The most advanced type, fully immersive VR aims to create a realistic, all-encompassing experience. Users wear headsets and may use motion-sensing gloves or treadmills to interact with the virtual environment. This category has seen significant progress in gaming and healthcare, offering users lifelike experiences in a completely virtual world. Some systems even incorporate tactile sensations, using haptic feedback to simulate touch and physical presence.
- Collaborative VR: In collaborative VR, people from different locations can come together in a shared virtual environment. Each participant is represented by an avatar, and communication occurs via microphones or headsets. This form of VR is commonly used for remote teamwork, meetings, and social interactions.
- Augmented Reality (AR): While technically different, AR is often grouped with VR. AR overlays virtual elements on top of the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. For example, AR apps allow users to visualize how furniture would look in their living rooms by projecting virtual 3D models of furniture onto their phones.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Mixed reality blends elements of both the physical and virtual worlds, enabling real-time interaction with digital objects that coexist with physical ones. It offers more interaction and immersion than AR, making it a distinct yet related technology in the XR (Extended Reality) space.
Core Features of Virtual Reality
Virtual reality stands out due to several defining characteristics that make it an interactive and immersive medium. The primary features of VR include:
- Immersion: The ability to transport users into a digital world that feels real, with sensory experiences that mimic the real world.
- Interaction: Users can manipulate objects, navigate through environments, and interact with the virtual world in real-time.
- Realistic Visuals: High-definition graphics and 3D rendering techniques produce lifelike visuals that contribute to the sense of presence.
- Spatial Audio: Sounds are placed realistically within the environment, enhancing the immersive experience.
- Haptic Feedback: Advanced systems simulate tactile sensations, allowing users to “feel” interactions within the virtual environment, from the sensation of holding objects to experiencing force feedback.
- 360-Degree Views: Most VR systems provide a full 360-degree field of view, enabling users to look in all directions and fully explore virtual spaces.
- Adaptive Environments: Using AI, VR environments can adjust in real-time to a user’s actions, offering a more personalized and dynamic experience.
Key Applications of Virtual Reality
While VR is most commonly associated with gaming, its applications extend far beyond entertainment. Industries worldwide are exploring the potential of VR in various fields, including:
- Training and Simulation: VR allows users to simulate real-world situations in a safe, controlled manner. This is particularly valuable in high-risk sectors such as healthcare, aviation, and military training. For example, surgeons can practice procedures in a virtual environment, while pilots can train in flight simulators.
- Education: VR is transforming education by enabling immersive learning experiences. Students can explore historical events, visit distant planets, or experience scientific concepts in 3D without leaving the classroom.
- Healthcare: VR is making significant strides in healthcare, from treating mental health disorders like PTSD and anxiety to assisting in physical rehabilitation. Medical professionals can also use VR to visualize patient anatomy in ways that traditional methods cannot.
- Retail: Virtual reality is revolutionizing the retail experience. Customers can try on clothes virtually, design their homes, or even walk through 3D stores before making a purchase. Virtual showrooms and product demos are changing the way people shop.
- Real Estate: Virtual reality offers potential buyers and renters the ability to tour homes and properties remotely. Architects and designers can also use VR to visualize designs before construction begins, making it easier to make adjustments.
- Entertainment: The entertainment industry is heavily invested in VR. Gaming is just the beginning; VR is set to transform how we experience movies, concerts, and even live sports events, by putting users in the heart of the action.
- Architecture and Design: VR allows architects to build and display designs in immersive 3D, offering clients the chance to walk through a building before it’s constructed. This leads to better decision-making and more accurate designs.
The Future of Virtual Reality
The future of virtual reality looks promising, with continued advancements in hardware, software, and content creation. As VR becomes more affordable and accessible, it will continue to find applications across new industries. Some trends to watch for in the near future include:
- Increased Accessibility: As VR headsets become more affordable and integrated into mobile devices, more people will be able to experience VR. This will expand VR’s reach into new sectors such as education, healthcare, and enterprise.
- Hyper-Realistic Experiences: The development of advanced haptic feedback devices, improved graphics, and spatial audio will make VR experiences even more lifelike.
- Integration with Augmented Reality: The blending of AR and VR technologies will allow for even more immersive and interactive experiences, with applications in fields such as navigation, gaming, and healthcare.
- Virtual Workspaces: The future of work will include virtual environments where people can collaborate and meet in 3D spaces, enabling remote workers to feel more present and engaged.
Conclusion
Virtual reality is a rapidly evolving technology with transformative potential across multiple industries. From gaming and entertainment to healthcare and education, VR is paving the way for more immersive, interactive experiences that engage users in unprecedented ways. As technology advances, VR will continue to blur the line between the physical and digital worlds, creating new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.