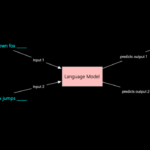
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to advance and become more integrated into various industries, it’s no secret that the job market is undergoing a significant transformation. While AI has the potential to automate many tasks, it also presents new opportunities for workers to upskill, reskill, and transition into emerging fields.
From Manual Labor to Machine Power: The Industrial Awakening
Human labor has undergone a radical transformation over the last few centuries. For most of recorded history, physical effort — often forced or unpaid — was the cornerstone of productivity. Societies were powered by slaves, serfs, and peasants, performing grueling work in fields, mines, and construction without autonomy or fair compensation.
️ The Machine Age Begins
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries marked the first major break from this cycle. Steam engines, looms, and factory machines began to amplify human effort, replacing sheer muscle with mechanical precision. This shift didn’t eliminate hardship — early factory workers toiled in horrific conditions — but it started a process of decoupling work from physical endurance.
Key effects:
-
Mechanization reduced dependence on raw human power
-
Urban migration spiked as people left farms for factories
-
Productivity soared, enabling mass production and global trade
From Slave Labor to Structured Compensation

Historically, most laborers were not paid in money — or paid extremely unfairly. Enslaved individuals, indentured servants, and exploited classes often had no rights or wages, only subsistence (if that).
The introduction of wage labor — especially hourly and piece-based systems — was revolutionary:
-
Factory owners paid workers based on hours worked or items produced
-
Labor laws emerged to protect workers from abuse
-
The idea of a “living wage” and the 40-hour workweek began to take shape
This era introduced basic worker dignity, and the idea that time has value. With the rise of unions, benefits, and minimum wage laws, workers gradually gained economic and political power.
How Henry Ford Took Advantage of Industrialization — And Changed the World
The Industrial Revolution introduced steam engines, mechanized tools, and early factories — but it was Henry Ford who systematized these innovations to launch a new era of mass production and mobility.
The Problem Before Ford
In the early 1900s:
-
Cars were luxury items, hand-built, and expensive
-
Manufacturing was slow, inconsistent, and labor-intensive
-
Only the wealthy could afford automobiles
Industrialization had brought machines, but efficiency was still limited.
Enter Henry Ford: The Industrial Visionary
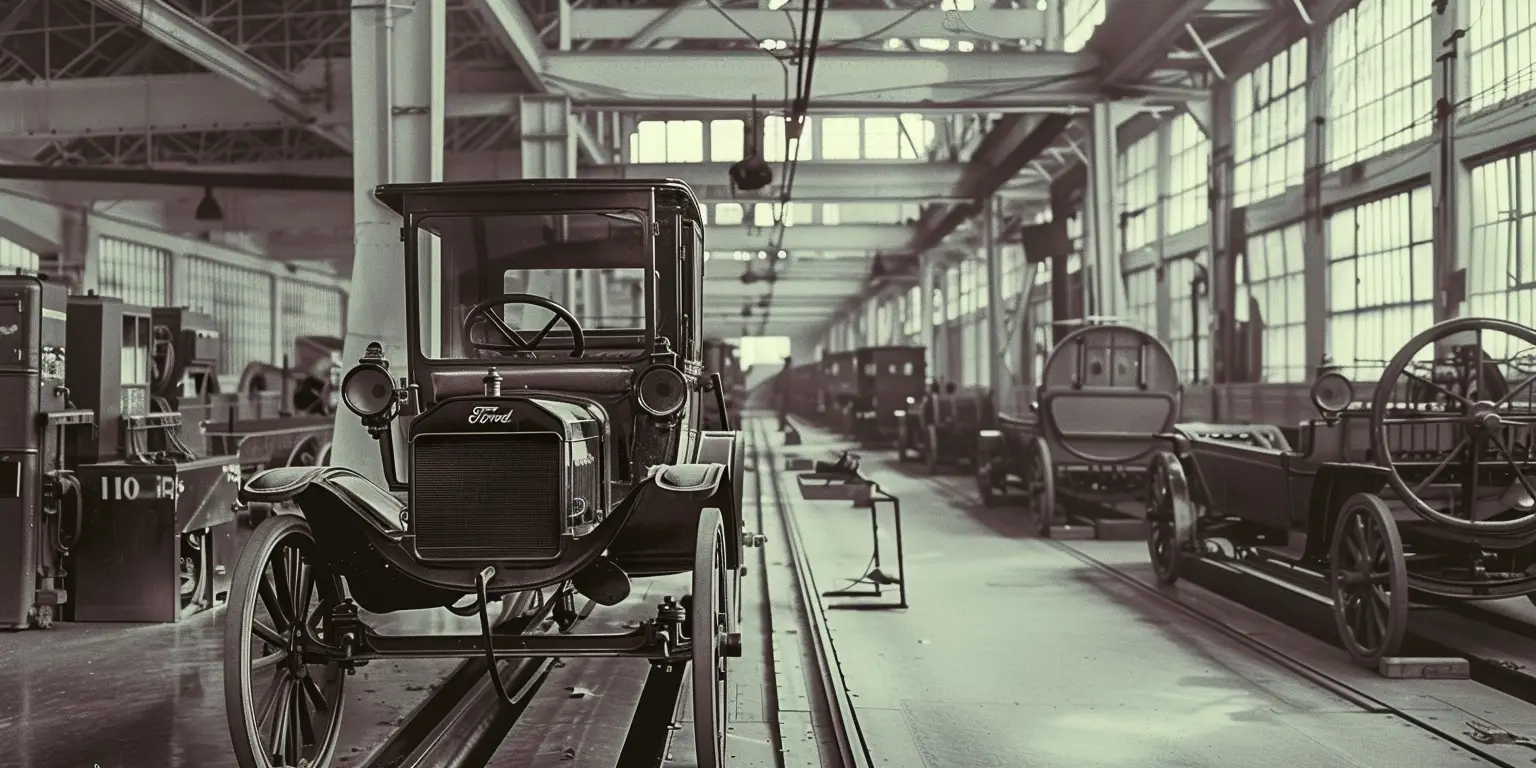

In 1913, Henry Ford introduced the moving assembly line in his Highland Park factory — a breakthrough that:
-
Reduced production time of a Model T from 12 hours to just 90 minutes
-
Slashed the cost per vehicle, making it affordable to average Americans
-
Allowed scale and standardization, producing over 15 million cars in two decades
️ What Made Ford’s Strategy Revolutionary?
✅ 1. Assembly Line Manufacturing
-
Ford applied the principle of division of labor: each worker did one task, repeatedly
-
Conveyor belts moved parts to the worker, not the other way around
-
This drastically boosted speed and precision
Inspired by meatpacking lines in Chicago, Ford turned a chaotic build process into a mechanical flow.
✅ 2. Vertical Integration
-
Ford owned the supply chain: steel mills, rubber plantations, railroads
-
He controlled costs and ensured consistent quality
-
No outsourcing delays — it was all in-house
✅ 3. Mass Market Vision
-
Ford’s goal wasn’t just to build cars — it was to put every American on wheels
-
His Model T was affordable, simple, and durable
-
He created a product for the masses, not the elite
✅ 4. Worker-Centric Pay (Strategically)
-
In 1914, Ford doubled factory wages to $5/day
-
Why? To reduce turnover, boost morale, and create a class of workers who could afford the products they built
-
This was a brilliant feedback loop: build the product → pay the workers → workers become customers
Global Impact of Ford’s Industrialization Strategy
-
Standardized mass production became the norm — from cars to appliances to electronics
-
Created the blueprint for the modern factory system
-
Inspired entire industries to rethink efficiency, logistics, and labor
-
Sparked urban growth, infrastructure development, and consumer culture
“If I had asked people what they wanted, they would have said faster horses.”
— Henry Ford
From Ford’s Assembly Line to AI Automation
Just as Henry Ford leveraged the industrial tools of his era to scale production and reshape society, today’s innovators are using AI, data, and robotics to do the same for knowledge and labor.
Ford’s legacy isn’t just in cars — it’s in how he made innovation accessible to everyone.
AI and the New Cognitive Revolution

Today, we’re entering a new industrial revolution, not powered by steam, but by algorithms. AI is transforming work once again — but now it’s not just physical labor being replaced. It’s mental tasks too:
-
AI writes, analyzes, diagnoses, forecasts, and even designs
-
Routine jobs — not just manual ones — are becoming automated
-
Gig work, remote work, and freelance AI platforms are reshaping how people earn
What This All Means
-
From slavery to wage labor, humanity made a leap in dignity
-
From muscle to machine, productivity exploded
-
From routine tasks to AI, we’re now being pushed into roles that require creativity, emotional intelligence, and lifelong learning
How Work Success Has Evolved — From Hunting to Algorithms
The way humans define success at work has changed dramatically over time — shaped by our tools, environments, and societal values. What mattered in one era would be irrelevant or even inefficient in another.
Let’s compare each stage:
1. Hunter-Gatherer Era
Success = Survival
-
Measured by: Food gathered, animals hunted, territory protected
-
Skills valued: Speed, strength, instinct, collaboration
-
Outcome: Feed your tribe or starve. Survival was the metric.
Lesson: Work was directly tied to immediate life or death outcomes.
2. Agrarian Age (Farming Revolution)
Success = Yield and Land
-
Measured by: Acres farmed, harvest size, livestock owned
-
Skills valued: Endurance, weather knowledge, seasonal planning
-
Outcome: The more you grew, the more stable your life became.
Lesson: Work was about ownership and long-term stability. Labor was physical and local.
3. Industrial Age
Success = Output and Obedience
-
Measured by: Hours worked, items produced, following rules
-
Skills valued: Punctuality, discipline, repetition
-
Outcome: You earned a wage, rose in ranks through loyalty and hard work.
Lesson: Work became about efficiency, systems, and structure — not survival.
4. Information Age
Success = Knowledge and Speed
-
Measured by: Emails sent, projects delivered, KPIs hit
-
Skills valued: Communication, analysis, tech literacy
-
Outcome: The smartest and fastest thinkers got ahead.
Lesson: Work shifted to the mind — and digital tools extended human capability.
5. AI-Powered Age (Now & Next)
Success = Creativity + Strategic Thinking + AI Leverage
-
Measured by:
-
Can you ask better questions than AI can answer?
-
Can you design systems, not just follow them?
-
Can you combine human nuance with machine scale?
-
-
Skills valued:
-
Prompt engineering, domain expertise, emotional intelligence, problem-solving, adaptability
-
Lesson: We’ve moved from labor to logic — and now from logic to leverage.
You’re not just doing the work — you’re designing the system that does the work.
The Rise of the Internet — And Who Gained the Most

The internet is the most transformative invention of the last century. It connected the world, digitized knowledge, redefined communication — and created unprecedented economic winners.
Let’s break down how it rose, and who cashed in.
⚡ The Internet’s Evolution at a Glance
| Era | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1969 | ARPANET launched | First packet-switched network (U.S. military) |
| 1983 | TCP/IP standard | The foundation of modern networking |
| 1991 | World Wide Web goes public | Invented by Tim Berners-Lee |
| 1995–2005 | Dot-com boom | Rapid growth in websites, e-commerce, browsers |
| 2005–2015 | Social media era | Facebook, YouTube, Twitter explode |
| 2015–Now | Cloud, mobile & AI | The internet everywhere — always connected |
Who Gained the Most?
1. Big Tech Companies — The Platform Kings
-
Google became the gateway to the world’s information
-
Amazon turned into the global mall
-
Facebook/Meta monetized human connection
-
Apple brought the internet to your pocket
-
Microsoft powered the infrastructure behind it all
These companies became trillion-dollar giants because they didn’t just use the internet — they built on top of it and shaped how others accessed it.
2. Entrepreneurs & Developers — The Builders
-
People like Jeff Bezos, Elon Musk, Sergey Brin, and Mark Zuckerberg built platforms that scaled with the web
-
Countless developers created tools, plugins, SaaS apps, and websites
-
Open-source contributors laid the groundwork for millions of digital products
Those who understood how to solve real-world problems online became the new business elite.
3. Digital Natives & Creators — The New Class of Influencers
-
Bloggers, YouTubers, Instagrammers, and TikTok creators gained massive global audiences
-
People who once needed a publisher, studio, or TV station could now reach millions directly
-
The creator economy is now worth over $250 billion
The internet gave distribution power to individuals for the first time.
4. Investors & Early Adopters — Those Who Bet Early
-
VC firms like Sequoia, Andreessen Horowitz, and SoftBank made billions backing internet companies early
-
Anyone who bought Amazon or Google stock in the early 2000s saw unimaginable returns
-
Domain squatters, affiliate marketers, early eBay sellers — all found gold in the digital frontier
Being early wasn’t luck — it was vision + risk + execution.
Who Missed Out?
-
Traditional companies that failed to go online (e.g. Blockbuster, Kodak)
-
Print media, retail giants, and legacy banks who didn’t adapt fast enough
-
Countries and regions without early internet access — widening the digital divide
The Takeaway
The biggest winners of the internet were the builders, the platform owners, and the early movers.
The same pattern is happening again — but now with AI.
-
In the 2000s, the question was: “Do you have a website?”
-
In the 2020s, it’s: “Do you have an AI strategy?”
The next Google, Amazon, or Facebook will be built on top of AI.
And those who missed the internet wave now have a second chance — if they move fast.
What This Means for You
The most successful people today won’t just work hard.
They’ll work smart — by using AI as a co-worker, not a competitor.
In the AI era:
-
Creativity > compliance
-
Systems > sweat
-
Leverage > labor
We’ve gone from surviving with our hands to thriving with our minds — and now we’re building with machines that think.
The Rise of Automation
One of the most significant impacts of AI on employment is the increased use of automation. Machines and algorithms can perform tasks faster, more accurately, and at a lower cost than humans. This has led to the displacement of certain jobs, particularly those that involve repetitive or routine tasks. However, AI also creates new job opportunities in areas such as:
- AI Development and Maintenance: As AI becomes more prevalent, companies need professionals to design, develop, and maintain AI systems.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: AI generates vast amounts of data, and workers with skills in data analysis and interpretation are in high demand.
- Customer Service and Experience: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are changing the way companies interact with customers, creating new opportunities for workers in customer service and experience design.
New Job Categories
The rise of AI has also led to the creation of new job categories that didn’t exist before. Some examples include:
- AI Ethicist: Professionals who ensure that AI systems are fair, transparent, and unbiased.
- Data Scientist: Experts who collect, analyze, and interpret complex data to inform business decisions.
- Human-Machine Interface Designer: Workers who design interfaces that enable humans and machines to work together seamlessly.
Upskilling and Reskilling
As AI continues to change the job market, it’s essential for workers to upskill and reskill to remain relevant. This can involve:
- Learning new programming languages: Familiarity with languages such as Python, R, and SQL can be beneficial for workers in data analysis and AI development.
- Developing soft skills: Skills such as communication, creativity, and problem-solving are becoming increasingly important in a world where AI is handling routine tasks.
- Pursuing continuous learning: Workers should be committed to ongoing learning and professional development to stay ahead of the curve.
The Future of Work
While AI presents challenges, it also offers opportunities for workers to adapt and thrive. As the job market continues to evolve, it’s essential to focus on:
- Lifelong learning: Workers should be committed to ongoing learning and professional development.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to new technologies and changing job requirements is crucial in a world where AI is increasingly prevalent.
- Creativity and innovation: As AI handles routine tasks, workers should focus on high-value tasks that require creativity, innovation, and problem-solving.
The future of work is uncertain, but one thing is clear: AI is changing the job market in profound ways. By embracing this change and upskilling, reskilling, and adapting to new technologies, workers can thrive in a world where AI is increasingly prevalent.
Jumping In Early on AI: Why It’s the Smartest Move You Can Make

⚙️ We’re at the Start of an Industrial Shift — Not the End
Artificial Intelligence is not just a trend — it’s the beginning of a technological epoch as transformational as electricity, the internet, or the printing press. But unlike past revolutions, AI is evolving at exponential speed.
If you jump in early:
-
You ride the wave, instead of being drowned by it.
-
You shape the tools, instead of being shaped by them.
-
You gain compound knowledge and career advantage over time.
Why Early Movers Win — In Careers, Business, and Tech
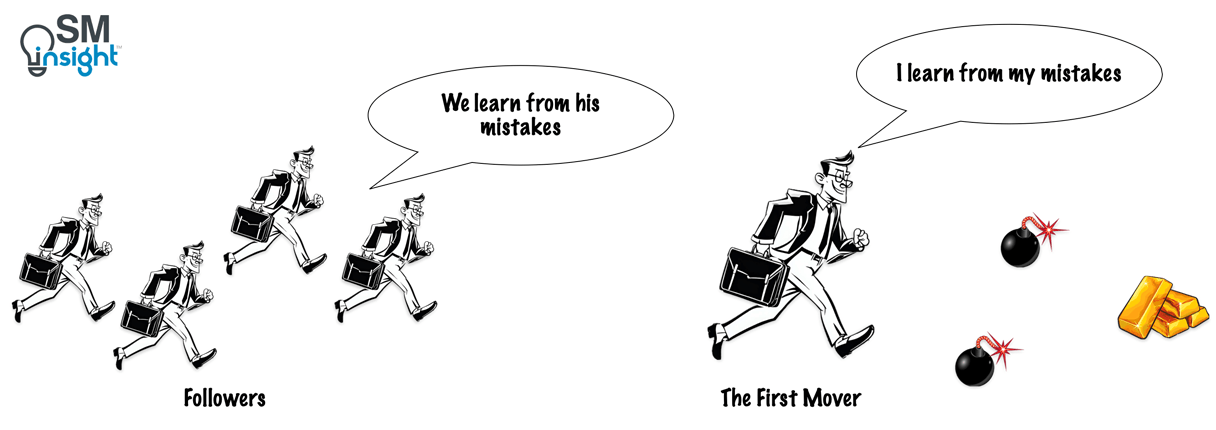
1. First Movers Learn Faster
AI is not something you understand overnight — it’s a deep field. Getting in early allows you to:
-
Learn about LLMs, agents, embeddings, vector stores
-
Understand what’s hype vs. what’s real
-
Build useful tools while others are still confused
Every week counts in a fast-moving field.
2. Early Builders Own the Market
Many of the biggest startups of tomorrow will be built today, in the AI space:
-
Early AI adopters are building personalized agents, automation platforms, smart tutors, tax assistants, and AI co-pilots
-
Tools like LangChain, HuggingFace, OpenAI APIs, and local models let you prototype fast
The earlier you enter, the easier it is to find untapped niches and build domain-specific AI systems.
3. AI Skills Are the New Literacy
Soon, knowing how to:
-
Write a prompt
-
Integrate an AI API
-
Use LangChain, RAG, or embedding models
…will be as basic as knowing Excel or Google Search. Those who don’t learn will be left behind in most knowledge-based jobs.
4. Early Adoption Reduces Risk Later
By experimenting now, you:
-
Understand the limitations and risks of AI
-
Build AI governance and trust frameworks
-
Create internal policy before regulations make it mandatory
Companies and individuals who lag behind will face steeper costs and legal friction later.
How AI Will Learn Manual Labor: Feeding It Human Experience
For centuries, manual labor — building, cleaning, driving, cooking, lifting — was the exclusive domain of human muscles and senses. While we’ve seen machines take over repetitive tasks in factories, the next wave of progress is even more profound:
AI is being trained to learn physical labor the same way we did — through experience.
Step 1: Capture Human Movements as Data
Modern sensors, wearables, and cameras are being used to record how humans perform physical tasks:
-
Robots observe humans stacking shelves, flipping burgers, tying knots, or walking across uneven terrain
-
Motion capture suits record body posture, muscle coordination, grip strength, and balance
-
Video datasets of people doing tasks are labeled frame-by-frame to teach machines step-by-step sequences
This is the digital apprenticeship era — where AI doesn’t read manuals, it watches humans do the job.
Step 2: Feed Experience into AI Models
The data captured above becomes training input for models:
-
Computer vision + imitation learning: The robot sees, learns, then replicates
-
Reinforcement learning: AI agents try tasks repeatedly in simulation or real life until they succeed
-
Foundational robotic models (like OpenAI’s RoboGym, Tesla’s Optimus, or Google DeepMind’s RT-2) are trained on millions of experiences across different environments
AI begins to generalize: “If I can grip this object, I can likely grip that one too.”
️ Step 3: Combine AI + Robotics to Execute Tasks
Once trained, the AI is embedded into robotic bodies:
-
Arms that paint, hands that fold laundry, legs that walk on uneven ground
-
Autonomous warehouse bots, delivery drones, robotic nurses, construction droids
Robots powered by AI are not hardcoded — they adapt, thanks to their training on human experiences.
⚙️ Real-World Examples
-
Tesla Optimus: Trained to sort, carry, and manipulate objects with human-like precision
-
Boston Dynamics + AI: Robots can now run, flip, and even dynamically adjust balance
-
Amazon warehouses: Robotic arms trained to pick millions of different objects
-
Figure AI: Building general-purpose humanoid robots trained by watching humans work
Why This Matters
This isn’t just about automation — it’s about encoding human dexterity, judgment, and adaptability into machines. For the first time in history:
-
Machines aren’t just strong — they’re learning to be skilled
-
Manual labor won’t require flesh and blood — it’ll require data and models
The Future of Physical Work
In the next decade:
-
Robots will learn from watching you work
-
A single worker may train a fleet of AI-powered machines
-
Companies will upload expertise like software updates
Your hands teach the AI once — and it performs that job a million times, perfectly.
Final Thought: The AI Gap Will Only Grow
There’s a saying in tech:
“The best time to start was yesterday. The second-best time is now.”
Early adopters of AI will own the tools, the workflows, and the mindset that the rest of the world will eventually have to catch up to.
If you’re thinking of waiting — don’t. The AI train is already moving. The question is: will you be a passenger, an engineer, or left at the station?
How to Get Started with AI: Tools You Can Use Every Day
The AI revolution is here — but the good news is, you don’t need a PhD to participate. Whether you’re a student, entrepreneur, freelancer, or knowledge worker, there are AI tools you can start using right now to boost your productivity, creativity, and career.
✅ Step 1: Understand the AI Basics (No Code Needed)
Before diving into tools, get a clear idea of what modern AI can do:
-
Generative AI creates content (text, code, images, etc.)
-
Language models like GPT understand and respond to human prompts
-
Embeddings & search power tools that retrieve relevant info
-
Agents combine tools, memory, and logic to perform tasks autonomously
A few free resources:
-
YouTube: Two Minute Papers, Fireship, or The AI Epiphany
️ Step 2: Use These AI Tools in Your Daily Workflow
1. ChatGPT / Claude / Gemini (Everyday AI assistant)
-
Write emails, brainstorm ideas, summarize documents
-
Great for research, technical explanations, content creation
Free tools:
2. Notion AI / Microsoft Copilot / GrammarlyGO (Productivity tools with AI built-in)

-
Notion AI: Write, summarize, automate meeting notes
-
Microsoft Copilot: Use AI in Word, Excel, Outlook
-
GrammarlyGO: Write and rewrite smarter
These tools blend into your everyday work apps.
3. Perplexity.ai (AI-powered search engine)
-
Ask questions and get reliable, sourced answers
-
Great for research, fact-checking, or summaries
4. Zapier AI / Bardeen / Reclaim.ai (Automate repetitive tasks)
-
Connect tools like Gmail, Slack, Notion, Calendar
-
Automate workflows: “If I get this email, send it to my team”
AI + automation = time saved.
5. GitHub Copilot / Codeium / TabNine (For coders)
-
Autocomplete code, suggest fixes, write functions from comments
-
Great for developers, learners, and hobby coders
⚙️ Step 3: Learn a Simple No-Code AI Workflow
You can build useful AI apps without coding, using tools like:
-
Flowise – drag-and-drop LLM workflows
-
Zapier + OpenAI – trigger LLMs from forms, messages, etc.
-
Airtable + AI – organize prompts, content, and data
Bonus: Want to Go Deeper?
Once you’re ready to build your own tools:
-
Learn Python, LangChain, and Streamlit
-
Use free models like LLaMA 3, Mistral, or Gemma
-
Explore Hugging Face for model exploration and hosting
Final Thought
You don’t have to wait for a course or a company to “train” you.
You can use AI right now, today, with free tools to solve real problems.
The key is not just to consume AI — but to interact with it, experiment, and build a habit.
Final Message: Start Small, Start Now

The AI revolution isn’t coming — it’s already here. The people and organizations who embrace it early will shape the future, not just react to it.
You don’t need to be an expert to start. You just need:
-
Curiosity to explore new tools
-
Consistency to build habits
-
Courage to experiment and fail forward
Whether you’re a student, creator, entrepreneur, or employee — AI can amplify your abilities if you learn how to use it wisely.
The best way to prepare for the future is to build with it — today.
So open ChatGPT, try a workflow on Zapier, or automate one tiny task this week.
Start small. Stay curious. Move fast. The future favors the early.