Order, Dimension, Rank, Nullity, Null space, and Column space with a single worked example
Definitions (short)
* Order (size) of an $m\times n$ matrix: number of rows $m$ and columns $n$.
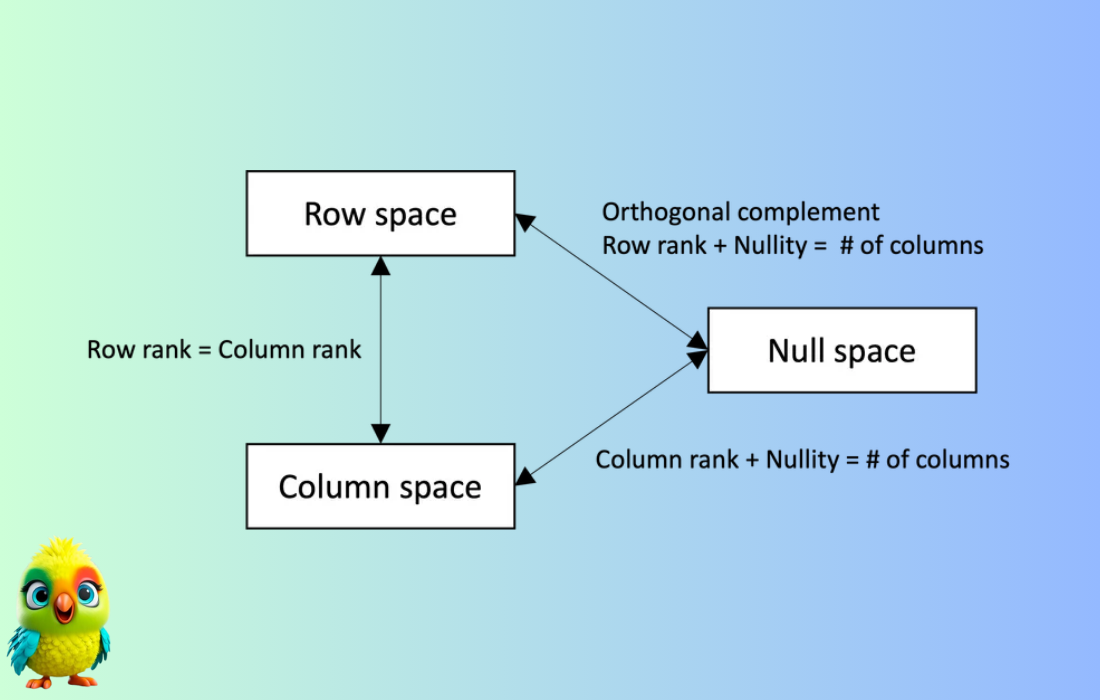
* Rank: the dimension of the column space (number of linearly independent columns).
* Nullity: the dimension of the null space (number of free variables in the solution of $A\mathbf{x}=0$).
* Rank–Nullity theorem: $\operatorname{rank}(A)+\operatorname{nullity}(A)=n$ (number of columns).
* Column space (Col A): span of the columns of $A$ — a subspace of $\mathbb{R}^m$.
* Null space (Nul A): solution set of $A\mathbf{x}= \mathbf{0}$ — a subspace of $\mathbb{R}^n$.
Let’s break down each concept step-by-step using the matrix:
$$
A = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 2 & 0 & 3 \\
0 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 3 & 1 & 4
\end{bmatrix}.
$$
1. Order (Size) of the Matrix
The order (or size) of a matrix is given by its number of rows and columns.
– For matrix A:
– Rows ($m$) = 3
– Columns ($n$) = 4
– Order: $3 \times 4$
2. Rank of the Matrix (Dimension of Column Space)
The rank of a matrix is the number of linearly independent columns (or rows).
To find it:
Step 1: Row-Reduce to RREF (Row Echelon Form)
Perform Gaussian elimination to convert $A$ into RREF:
$$
\text{RREF}(A) = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 0 & -2 & 1 \\
0 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0
\end{bmatrix}.
$$
Step 2: Identify Pivot Columns
– Pivot columns have leading 1s (first non-zero entry in a row).
– Here, columns 1 & 2 (first and second columns) are pivot columns.
Step 3: Rank = Number of Pivot Columns
– Rank(A) = 2
3. Nullity of the Matrix (Dimension of Null Space)
The nullity is the number of free variables in the solution to $A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{0}$.
Step 1: Use the Rank-Nullity Theorem
The theorem states:
$$
\text{Rank}(A) + \text{Nullity}(A) = n \quad (\text{number of columns})
$$
– Here, $n = 4$
– $\text{Rank}(A) = 2$
– So, $\text{Nullity}(A) = 4 – 2 = 2$
Alternative: Find Null Space Explicitly (Next Section)
The nullity is the number of vectors in the null space basis.
4. Null Space (Solution to $A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{0}$)
The null space consists of all vectors $\mathbf{x}$ such that $A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{0}$.
Step 1: Write System of Equations from RREF
From $\text{RREF}(A)$:
$$
\begin{cases}
x_1 – 2x_3 + x_4 = 0 \\
x_2 + x_3 + x_4 = 0
\end{cases}
$$
Step 2: Express Pivot Variables in Terms of Free Variables
– Pivot variables: $x_1, x_2$
– Free variables: $x_3, x_4$
Let $x_3 = s$, $x_4 = t$ (arbitrary parameters).
Then:
$$
x_1 = 2s – t, \quad x_2 = -s – t
$$
Step 3: Write General Solution
$$
\mathbf{x} = \begin{bmatrix}
2s – t \\
-s – t \\
s \\
t
\end{bmatrix}
= s \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} + t \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ -1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}
$$
Step 4: Basis for Null Space
The two vectors form a basis:
$$
\text{Nul}(A) = \text{Span}\left\{ \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ -1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \right\}
$$
– Nullity = 2 (matches earlier result).
5. Column Space (Span of Pivot Columns)
The column space is the span of the linearly independent columns of $A$.
Step 1: Identify Pivot Columns in Original Matrix
From RREF, pivot columns are 1 & 2, so we take columns 1 & 2 of $A$:
$$
\text{Col}(A) = \text{Span}\left\{ \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} \right\}
$$
– Dimension of Col(A) = Rank(A) = 2
6. Verification: Rank-Nullity Theorem
– Rank(A) = 2
– Nullity(A) = 2
– Number of columns (n) = 4
– Check: $2 + 2 = 4$ ✔️
Summary
| Concept | Result |
|---|---|
| Order | $3 \times 4$ |
| Rank | $2$ (dimension of column space) |
| Nullity | $2$ (dimension of null space) |
| Null Space Basis | $\left\{ \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ -1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \right\}$ |
| Column Space Basis | $\left\{ \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} \right\}$ |
| Rank-Nullity Check | $2 + 2 = 4$ ✔️ |
Final Answer
For the matrix
$$
A = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 2 & 0 & 3 \\
0 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 3 & 1 & 4
\end{bmatrix},
$$
we have:
– Order: $3 \times 4$
– Rank: $2$
– Nullity: $2$
– Null Space Basis: $\left\{ \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ -1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \right\}$
– Column Space Basis: $\left\{ \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} \right\}$
This method applies to any matrix – just follow the steps!